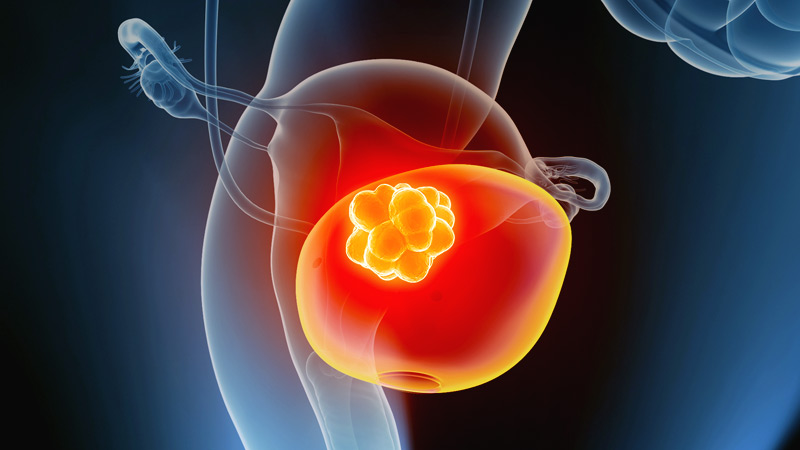
Bladder is an organ present in the pelvic area, which is similar to a balloon in shape. It is responsible to store urine. Bladder cancer usually starts in cells that are found in the inner linings of the bladder.
Generally, older adults are affected by this problem. However, it may occur in people belonging to any age group. In most cases, bladder cancer is diagnosed in the initial stages when it isn’t very difficult to treat it. However, it is quite possible that bladder cancer may reoccur in patients. This is why most sufferers of this disease prefer going for follow-up screenings even after years of their treatment of the disease.
Symptoms of Bladder Cancer
This is the sixth most common cancer type in USA. Some of the symptoms of bladder cancer are:
- Blood in urine
- Lower back pain
- Feeling the frequent urge for urination
- Pain while you urinate
Not to forget, smoking is a big risk factor. Exposure to some specific chemicals at the workplace is another factor that increases the risk of patients suffering from bladder cancer and worsens their condition even more. Elder white people and male of any skin type are also at a higher risk for suffering from this kind of cancer.
Reasons for Bladder Cancer
The bladder that contains urine grows smaller or larger according to the quantity of urine that it is holding. Urine flows from kidneys into the bladder via ureters. From here, it is excreted from the body with the help of a narrow tube known as urethra.
Bladder cancer takes place when healthy cells does not behave in their normal way and instead of growing and dividing in a systematic way, they develop mutations and thereby grow in an unmanageable way and do not die. As a result, these unmanageable cells further forms tumor.
Different Bladder Cancer’s
There are various kinds of cells present in the bladder that can become malignant. So, it is important to know the kind of cell that has caused the bladder cancer so as to know the treatment which would suit the patient in his current condition. Some of the bladder cancers are: squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma and transitional cell carcinoma.
Diagnosis and tests
Some of the common procedures and tests that are advised by doctor’s to the bladder cancer patients are: test for urine to observe the presence of cancer cells in it, looking inside the bladder with the help of a scope and imaging tests.
Stages of Bladder Cancer
Once it has been confirmed that a patient has bladder cancer, addition tests such as bone scan, CT scan, chest X-ray and magnetic resonance imaging may be suggested by the physician to know the stage of the disease of the patient.
Stages of bladder cancer are as given below:
- Stage I – In this stage, the cancer has only developed in the inner lining of the bladder and hasn’t involved muscular bladder wall as yet.
- Stage II – Here, the bladder wall has been invaded by the cancer.
- Stage III – This stage involves the spread of the cancer cells to the tissue that surrounds the bladder wall. They may have spread a little further to vagina or uterus in women or prostate in men.
- Stage IV – Lymph nodes and organs like liver, bones and lungs are also invaded by the cancer cells at this stage.
Surgical procedures are the most common treatments available for bladder cancer patients and are determined in accordance with the stage of the cancer of the patient.